The world urgently needs more STI vaccines
And better, faster, less expensive testing tools to reduce the toll of STIs.
In the News

Why We Need STI Vaccines and Diagnostics
Left untreated, STIs can lead to infertility, pregnancy complications, and cancer, and can increase the risk of HIV.
STIs often go undiagnosed and untreated. Despite their potentially devastating consequences, they may cause few or no immediate symptoms. And diagnosis can be inconvenient, unaffordable, or unavailable.
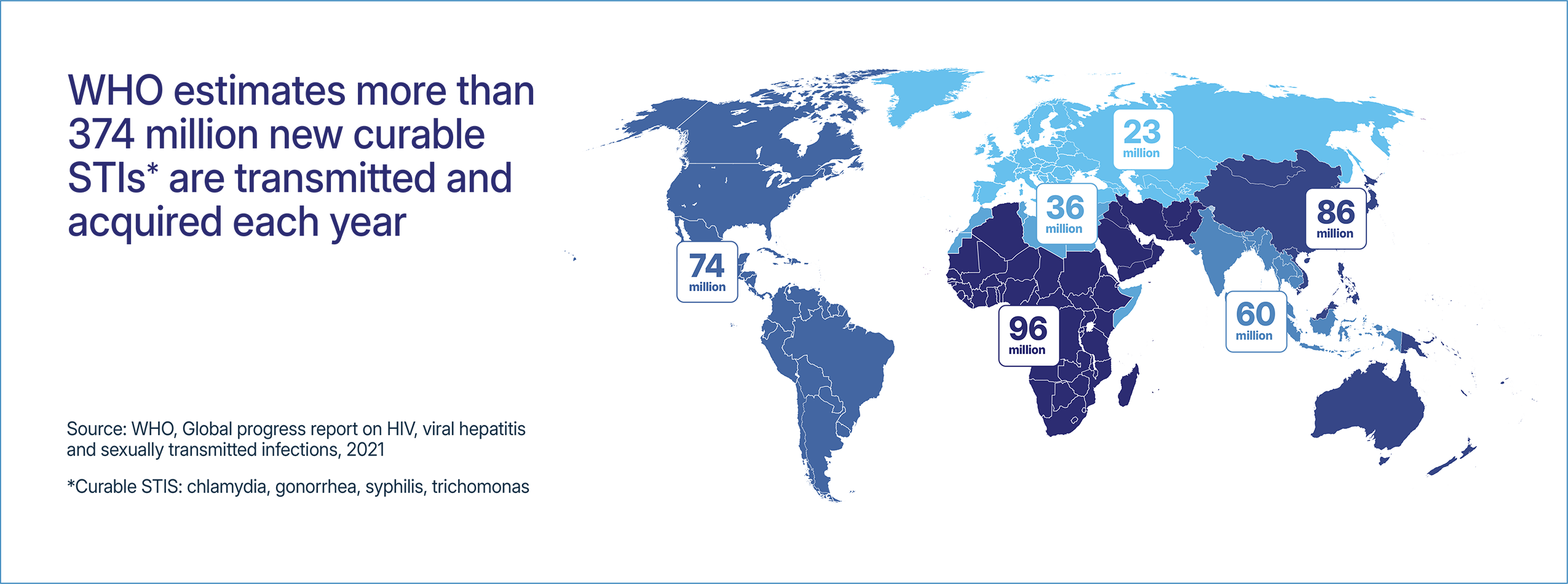
Learn about prevention, detection, and treatment options for common STIs
Click for advocacy needs and the latest on vaccines, diagnostics, and treatment for each pathogen.
How To Test for STIs
Some STIs, like chlamydia and gonorrhea, can be quickly diagnosed at a clinic or even through self-collection kits, when available. Expensive, time-consuming laboratory tests are required to diagnose many other common STIs.
Visit individual pathogen pages to learn more about diagnostics.

Global Investment Falls Short
Read AVAC’s 2022 review tracking funding trends in vaccine and diagnostics R&D, and pipeline investments for some of the most common STIs.
Worldwide Prevention, Shared Protection
This issue brief describes the impacts of the elimination and reduction of funding that supports STI research, testing, and prevention programming. This funding is critically important as STI rates continue to increase globally with more than 1 million curable STIs acquired every day. Without appropriate testing, treatment, and prevention programs, there is a risk that STI rates will continue to increase leading to more cases of infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and cancers.